[ad_1]
NVIDIA will present various developments in visualization, simulation, and creative AI at SIGGRAPH 2024, the leading computer graphics event scheduled for July 28 – Aug. 1 in Denver.
Over 20 research papers from NVIDIA will introduce innovative approaches advancing synthetic data generation and reverse rendering tools, aiding in the training of next-gen models. NVIDIA’s AI research aims to enhance simulation quality and unlock new avenues for constructing 3D representations of real or imaginative worlds.
The papers delve into diffusion models for generative visual AI, physics-based simulation, and progressively realistic AI-driven rendering. They encompass two recipients of the esteemed Best Paper Award as well as collaborative efforts with universities in the U.S., Canada, China, Israel, and Japan, along with researchers from companies like Adobe and Roblox.
These endeavors will facilitate the creation of tools that developers and companies can utilize to craft intricate virtual objects, characters, and environments. Synthetic data generation can be leveraged to narrate compelling visual tales, enrich scientists’ comprehension of natural phenomena, or support the simulation-based training of robots and self-driving vehicles.
Enhancing Texture Painting and Text-to-Image Generation with Diffusion Models
Diffusion models, a favored tool for converting textual prompts into images, can expedite the creation of visuals for storyboards or production, aiding artists, designers, and creators in bringing ideas to life faster.
Two papers authored by NVIDIA are propelling the capabilities of these generative AI models.
ConsiStory, a joint effort between NVIDIA researchers and Tel Aviv University, streamlines the generation of multiple images featuring a consistent main character, an essential feature for storytelling applications like illustrating a comic strip or outlining a storyboard. The team’s methodology introduces a novel approach termed subject-driven shared attention, reducing the time needed to create consistent imagery from 13 minutes to approximately 30 seconds.

NVIDIA researchers previously received the Best in Show recognition at SIGGRAPH’s Real-Time Live event for AI models transforming text or image prompts into custom textured materials. This year, they present a paper that applies 2D generative diffusion models to interactive texture painting on 3D meshes, allowing artists to paint in real time with intricate textures based on any reference image.
Initiating Advances in Physics-Based Simulation
Visual researchers are bridging the gap between physical entities and their digital counterparts through physics-based simulation — a spectrum of methodologies to replicate how digital objects and characters behave akin to the real world.
Several NVIDIA Research papers showcase breakthroughs in this domain, including SuperPADL, a project addressing the challenge of simulating intricate human movements driven by textual cues (see video at the top).
By combining reinforcement learning with supervised learning, the researchers exhibited how the SuperPADL framework could learn and replicate over 5,000 skills in real time on a standard NVIDIA GPU.
Another NVIDIA paper proposes a neural physics model utilizing AI to predict how objects, represented as a 3D mesh, a NeRF, or a solid object generated through text-to-3D models, would interact when moved in an environment.
A collaborative paper with researchers from Carnegie Mellon University introduces a groundbreaking renderer that, instead of simulating physical light, can perform thermal analysis, electrostatics, and fluid dynamics. Recognized as one of the top five papers at SIGGRAPH, this method is easily parallelizable and eliminates the need for intricate model cleanups, opening possibilities to expedite engineering design iterations.
In the illustration above, the renderer conducts a thermal analysis of the Mars Curiosity rover, where maintaining temperatures within a specific range is crucial for mission success.
Additional simulation papers introduce a more effective methodology for modeling hair strands and a pipeline accelerating fluid simulation by 10 times.
Setting New Standards for Realistic Rendering and Diffraction Simulation
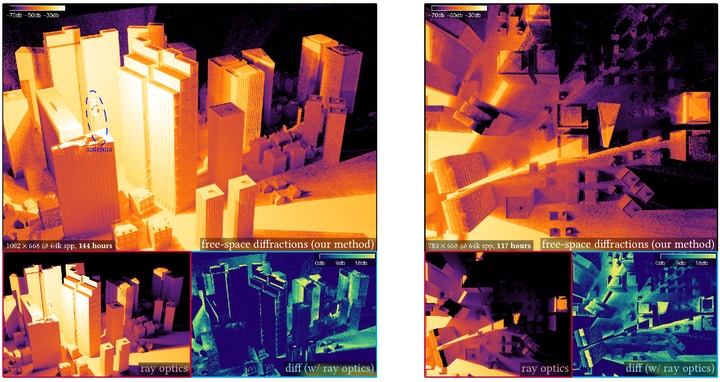
Another series of papers authored by NVIDIA introduce novel techniques to render visible light up to 25 times faster and simulate diffraction effects — such as those employed in radar simulations for autonomous vehicle training — up to 1,000 times quicker.
A paper by NVIDIA and University of Waterloo researchers addresses free-space diffraction, an optical phenomenon where light spreads out or bends around object edges. The team’s method seamlessly integrates with path-tracing workflows, enhancing the efficiency of diffraction simulation in complex scenes, providing up to 1,000 times acceleration. Beyond rendering visible light, the model holds potential to simulate longer wavelengths ofSonar, audio or wireless waves.
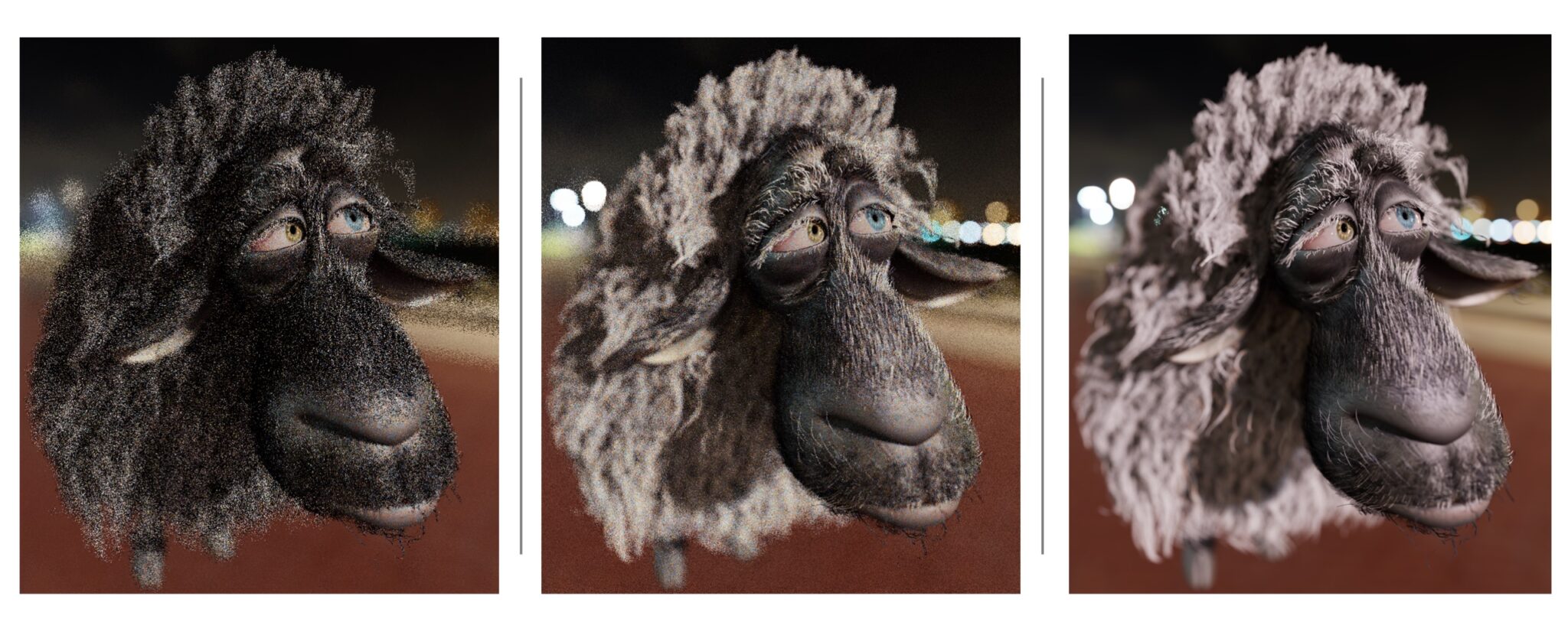
Tracing paths involves examining various routes — light rays bouncing multiple times through a setting — to craft a lifelike image. Two research papers from SIGGRAPH enhance the quality of sampling for ReSTIR, a ray-tracing technique initially presented by NVIDIA and Dartmouth College scholars at SIGGRAPH 2020, which has played a significant role in implementing ray tracing in games and other real-time visualization products.
One of these pieces, a joint effort with the University of Utah, presents a fresh approach to recycling computed routes that boosts effective sample count by up to 25 times, substantially enhancing image clarity. The other enhances sample quality by randomly altering a selection of the light’s trajectory. This aids in the superior performance of noise reduction algorithms, resulting in fewer visual defects in the ultimate rendering.

Teaching AI to Reason in 3D
NVIDIA researchers are also highlighting versatile AI utilities for 3D depictions and planning at SIGGRAPH.
One article introduces fVDB, a GPU-optimized framework for 3D profound learning that matches the magnitude of the physical world. The fVDB setup offers AI infrastructure for the vast spatial scale and sharp resolution of city-size 3D models and NeRFs, as well as the segmentation and reconstruction of extensive point clouds.
An acclaimed Best Technical Paper penned in partnership with Dartmouth College experts unveils a doctrine for illustrating the interactions of 3D objects with light. This doctrine consolidates an array of appearances into a single model.
Additionally, a joint project with the University of Tokyo, University of Toronto, and Adobe Research introduces an algorithm that generates seamless, voluminous curves on 3D meshes in real-time. Unlike prior methodologies that consumed hours, this structure operates within seconds and offers users extensive control over the results to allow interactive design.
NVIDIA at SIGGRAPH
Explore further about NVIDIA at SIGGRAPH, with exclusive functions including a conversational segment between NVIDIA pioneer and CEO Jensen Huang and Lauren Goode, chief essayist at WIRED, on the repercussions of automation and AI in business digitalization.
NVIDIA researchers will also present OpenUSD Day by NVIDIA, a comprehensive event displaying how developers and industry authorities are embracing and advancing OpenUSD to establish AI-driven 3D conduits.
NVIDIA Research consists of countless scientists and engineers globally, with squads dedicated to subjects like AI, computer graphics, computer vision, autonomous vehicles, and robotics. Witness more of their most recent works.
[ad_2]

